Picture a business networking dinner, wherein each participant gives an overview of their business, including target market, main products/services, and current concerns. You’ve been listening to some of the dozen or so professionals give concise overviews, and are taking notes – keenly interested in connecting with one or two (using Nicole’s Networking Advice), and thinking you might have some good feedback for a few others. Then it’s your turn, and you stand and give the “elevator pitch” you’ve honed to a thing of beauty. And… people look at you like you have two heads.
Picture a business networking dinner, wherein each participant gives an overview of their business, including target market, main products/services, and current concerns. You’ve been listening to some of the dozen or so professionals give concise overviews, and are taking notes – keenly interested in connecting with one or two (using Nicole’s Networking Advice), and thinking you might have some good feedback for a few others. Then it’s your turn, and you stand and give the “elevator pitch” you’ve honed to a thing of beauty. And… people look at you like you have two heads.
That has happened to both Nicole and me in recent weeks, and we were quite taken off guard! We thought we had worked hard to describe what we do (business process improvement) in a way that is easy to “get.” And we have, for the most part – just not in the elevator pitch (2-3 sentences) format that is crucial in networking events and casual conversation.
Clearly it’s something we need to work on.
One of the things that is so interesting to us, and has been since we started this business, is the varying degree of understanding (or lack thereof) of what “business process improvement” is. Being a process geek myself, I assume everyone is constantly thinking how they would improve things, and therefore inherently “gets” what business process improvement is. Not so!
Let’s start by defining a couple of terms:
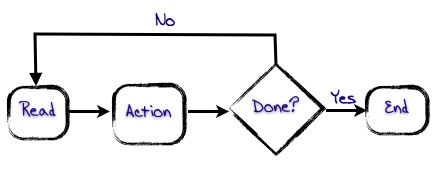
 A process can be defined as a series of actions or steps that are undertaken in order to achieve a particular outcome. Some common examples that may resonate with you – think of the steps that are involved in each:
A process can be defined as a series of actions or steps that are undertaken in order to achieve a particular outcome. Some common examples that may resonate with you – think of the steps that are involved in each:
- going through security screening at the airport
- filling out your year-end tax forms
- getting ready to leave the house each morning
- making a martini or a latte
- grocery shopping
When we say “business” process, we are referring to processes that happen every day at work in order to achieve a specific outcome. Do these sound familiar?
- recruitment
- performance evaluations
- business expense claims
- invoicing
- customer service
- production
- strategic planning
- approvals
- scheduling
Each of these (and dozens of others) happens every single day in most businesses, and if you’re lucky, they are smooth and efficient and wonderful and everything goes well all of the time and all your employees and customers are happy with them.
No? Well then.
If one of your business processes is somewhat less than perfect and causes you grief, if you go home on Friday night and think, “if only we didn’t have to do THAT thing,” if you get feedback from your customers that they are sick of having to do the same thing over and over with the same (unsatisfactory) results – well then my friend, you have a business process problem that needs improving.
Or, if you have an outcome or metric that is not performing as well as it should be, most likely there is a broken business process in there somewhere, and you need to figure out which one it is, uncover it, and fix it without adversely affecting any of the other processes that it impacts.
There are many ways to approach business process improvement – ours is one that focuses on engagement and leadership skills as a means of making improvements “stick.” It’s different than other more rigid methodologies, yet it uses elements from several of the most popular, including Six Sigma, Lean, Appreciative Inquiry, and Methods Time Measurement. We like to be professional and fun at the same time, and show people what business process improvement is, how it works, and how it can make their organizations better, faster, and cheaper.
Got it? Excellent. Now we just need to get that into an elevator pitch. Any suggestions? Tell us in the comments below!
Until next time,
Ruth.


 mething could go wrong, you’d be right. And how might that be a good thing? It can protect you from dangerous situations.
mething could go wrong, you’d be right. And how might that be a good thing? It can protect you from dangerous situations.
 respectfully, PFFT.
respectfully, PFFT.